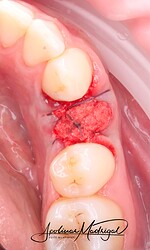
This Week in Dental Implants we are presenting an extraction case that utilizes piezosurgery and the Osteogen Plug to achieve clinical success. Piezosurgery can enhance the safety and efficacy of extractions. Please see the discussion below along with the references for more information on Piezosurgery.
Case Presentation: Atraumatic Extraction with Piezo and Osteogen
Case presentation by: Apolinar Madrigal, DDS, Trinity Dental and Implant Center
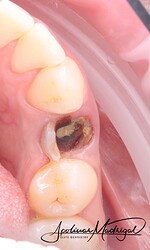
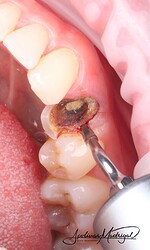
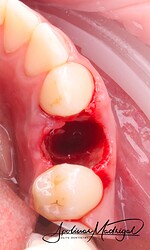
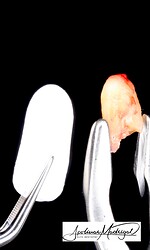
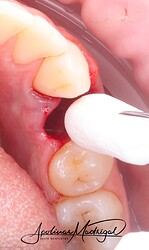
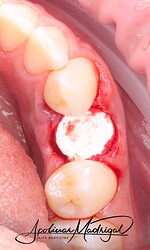
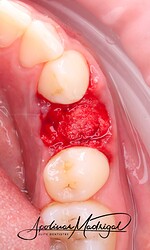
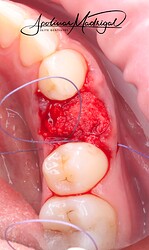
The patient presented with recurrent decay and fracture on a previously root canal therapy treated maxillary premolar. After clinical and radiographic evaluation, the tooth was determined to be non-restorable due to deep subgingival caries and structural compromise. We decided to extract the tooth and proceed with ridge preservation. I used a WH Piezo for an atraumatic extraction to preserve the buccal plate. After extraction and thorough socket debridement, we placed an OsteoGen Plug and sutured the site for closure.
Discussion: Why Piezosurgery for Atraumatic Extractions?
Piezosurgery was first introduced in dentistry in 1988 by the Italian oral surgeon Tomaso Vercellotti, who developed the Mectron® piezoelectric bone surgery unit. Piezosurgery minimizes damage to surrounding tissue by utilizing ultrasonic vibrations that selectively cut only mineralized hard tissues, such as bone, while sparing soft tissues. This technique operates at ultrasonic frequencies (typically between 25-30 kHz), which allows for precise and controlled cutting, reducing the risk of trauma to adjacent anatomical structures.
The piezoelectric osteotomy technique also creates a cavitation effect due to the cooling solution used during the procedure, which further enhances visibility and minimizes bleeding. This precision in cutting means that vital structures, such as nerves and soft tissues, are less likely to be harmed compared to conventional mechanical instruments that apply significant pressure and can cause unintended damage.
Piezosurgery offers several advantages for atraumatic extraction in dental procedures. This technique utilizes ultrasonic vibrations to precisely cut bone tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding soft tissues. The main benefits include:
-
Adjacent Soft Tissue Protection: Piezosurgery, when used as directed, decreases the chance of damage or cutting of adjacent soft tissue, while cutting through hard tissues.
-
Improved Visibility and Precision: The method provides better visibility in the surgical field and allows for precise and smooth cuts, which is crucial for atraumatic procedures.
-
Reduced Risk of Complications: By minimizing damage to soft tissues, piezosurgery reduces the risk of postoperative complications, such as swelling and pain.
-
Enhanced Patient Comfort: The technique results in less vibration and noise compared to conventional methods, improving patient comfort during the procedure.
References
Osseous response following resective therapy with piezosurgery., Tomaso Vercellotti , Marc L Nevins , David M Kim , Myron Nevins , Keisuke Wada , Robert K Schenk , Joseph P Fiorellini , The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry. Volume: 25, Issue: 6, 2005
A piezoelectric instrument vibrating in the ultrasonic frequency range was investigated for its potential use in periodontal resective therapy. The rate of postoperative wound healing (baseline and 14, 28, and 56 days after surgery) in a dog model following surgical ostectomy and osteoplasty was the marker used to compare the efficacy of this instrument (PS) with a commonly used carbide bur (CB) or a diamond bur (DB). The surgical sites treated by CB or DB lost bone, in comparison to baseline measurements, by the 14th day, while the surgical sites treated by PS revealed a gain in the bone level. By day 28, the surgical sites treated by all three instruments demonstrated an increased bone level and regeneration of cementum and periodontal ligament. However, by day 56, the surgical sites treated by CB or DB evidenced a loss of bone, versus a bone gain in the PS-treated sites. Thus, it appears that PS provided more favorable osseous repair and remodeling than CB or DB when surgical ostectomy and osteoplasty procedures were performed. Therefore, PS could be regarded as being efficacious for use in osseous surgery. Read MoreEnhancing precision and safety in dental surgery - the advantages of piezosurgery., Agnieszka Rolek , Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego. Volume: 52, Issue: 4, 2024
Piezosurgery in dentistry is an innovative surgical technique utilizing ultrasonic vibrations to precisely cut bone tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding soft tissues. This method is particularly advantageous for delicate procedures in oral and maxillofacial surgery, including bone graft harvesting, sinus lifts, and tooth extractions. Piezosurgery operates on the principle of piezoelectricity, discovered by Jacques and Pierre Curie in the 19th century, where a piezoelectric crystal converts oscillating electric fields into mechanical vibrations. Devices used in piezosurgery generate ultrasonic frequencies (25-30 kHz) that enable linear vibrations and controlled cutting, selective for mineralized tissues.The technology offers significant benefits over conventional surgical methods, including improved visibility, precise and smooth cuts, and a reduced risk of soft tissue damage. Clinical applications of piezosurgery demonstrate its effectiveness in preserving vital cells such as osteoblasts and osteocytes, promoting faster healing, and better osseointegration of implants. Specialized inserts and operating modes enhance its versatility for various surgical needs. Piezosurgery has shown to lower postoperative complications and enhance patient safety in complex procedures like sinus lifts and bone splitting. This advanced surgical technique represents a significant improvement in dental and oral surgery, offering enhanced precision, safety, and clinical outcomes, ultimately improving the standard of care and patient satisfaction. Read MorePiezosurgery in oral and maxillofacial surgery., G Pavlíková , R Foltán , M Horká , T Hanzelka , H Borunská , J Sedý , International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery. Volume: 40, Issue: 5, 2011
This review summarizes current knowledge and experience with piezosurgery, a promising, meticulous and soft tissue-sparing system for bone cutting, based on ultrasonic microvibrations. The main advantages of piezosurgery include soft tissue protection, optimal visibility in the surgical field, decreased blood loss, less vibration and noise, increased comfort for the patient and protection of tooth structure. To date it has been indicationed for use in oral and maxillofacial surgery, otorhinolaryngology, neurosurgery, ophthalmology, traumatology and orthopaedics. The main indications in oral surgery are sinus lift, bone graft harvesting, osteogenic distraction, ridge expansion, endodontic surgery, periodontal surgery, inferior alveolar nerve decompression, cyst removal, dental extraction and impacted tooth removal. In conclusion, piezosurgery is a promising technical modality for different aspects of bone surgery with a rapidly increasing number of indications throughout the whole field of surgery. Read More[Ultrasonic bone cutting in oral surgery: a review of 60 cases]., S Stübinger , C Landes , O Seitz , H-F Zeilhofer , R Sader , Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980). Volume: 29, Issue: 1, 2008
PURPOSE
Surgical reconstruction of bony defects in the oral cavity can often be challenging since thin and fragile bony structures are especially prone to fracture cased by bulky cutting tips or the application of significant pressure by conventional mechanical instruments. The risk of accidental damage to adjacent soft tissue structures, such as nerves, by a dental drill or saw is also extremely high. The use of modulated ultrasound (piezosurgery) makes it possible to overcome such complications as a result of the precise and minimally invasive surgery technique which is limited to mineralized hard tissue.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In 60 patients (38 male, 22 female) a piezosurgery device was used for different bone augmentation procedures before dental implant placement. The instrument uses modulated ultrasound (25 - 30 kHz) and the amplitude of the working tip ranges from 60 mum to 200 mum. The device was employed for sinus floor elevation (25), alveolar ridge augmentation using an autogenous block graft (25), alveolar ridge splitting (5) or lateralization of the alveolar nerve (5). Physiological sodium chloride was used as a cooling solution. For all osteotomies mode boosted burst c and pump 5 were used.
RESULTS
Piezoelectric osteotomy permitted micrometric selective cutting and a clear surgical site due to the cavitation effect created by the cooling solution and the oscillating tip. No excessive bleeding was encountered. The risk of accidental soft tissue harm, such as perforating the sinus membrane or damaging adjacent nerves, was definitely lower than in the case of a conventional bur. No serious complications were encountered in the postoperative wound healing process after 2, 14, 30 and 90 days. However, the surgical procedures were time-consuming.
CONCLUSION
Piezosurgery is an advantageous osteotomy technique for delicate structures in the oral and maxillofacial region. With respect to osteotomies of thin and fragile bones, the application of ultrasound is superior to other mechanical instruments because of the extremely precise and virtually arbitrary cut geometries, easy handling, efficient bone ablation and minimal accidental damage to adjacent soft tissue structures. Read More
A randomized controlled trial comparing conventional and piezosurgery methods in mandibular bone block harvesting from the retromolar region., Ferit Bayram , Ahmet Demirci , BMC oral health. Volume: 23, Issue: 1, 2023
BACKGROUND
Although piezosurgery is now commonly used for various applications in maxillofacial surgery, its advantages over conventional rotary instruments in terms of postoperative edema, ecchymosis, postoperative morbidity, and prolonged osteotomy time have been questioned.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study aimed to compare the efficiency, postoperative morbidity, and complication rates of piezosurgery and conventional methods in harvesting autogenous ramus grafts. In this randomized controlled trial, 21 patients (32 sides) underwent autogenous graft harvesting from the ramus area, with 16 sites treated using piezosurgery and 16 using the conventional method. The primary outcomes measured were osteotomy time, total operation time, and postoperative morbidity. Complication rates were also evaluated.
RESULTS
The final analysis encompassed 19 patients, accounting for a total of 30 donor sites, following the exclusion of two patients who were unable to attend the scheduled follow-up visits. A total of 19 patients (30 donor sites) were included in the final analysis. No statistically significant difference was found in the mean osteotomy time between the piezosurgery group (mean: 10.35, SD: 2.74 min) and the conventional group (mean: 8.74, SD: 2.74 min) (95% CI: -3.67 to 0.442, p = 0.119). The total operation time, postoperative pain, and swelling were not significantly different between the two groups (p > 0.05). The complication rates, including wound dehiscence and inferior alveolar nerve exposure, were similar in both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Piezosurgery can be safely used for harvesting autogenous ramus grafts and does not increase osteotomy or total operation time compared to the conventional method. The postoperative morbidity and complication rates were also similar, indicating that both techniques can be effectively employed in clinical practice.
CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION
The protocol was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (ID: NCT05548049, First registration date: 21/09/2022). Read More
Piezosurgery applied to implant dentistry: clinical and biological aspects., Cassiano Costa Silva Pereira , Walter Cristiano Gealh , Lamis Meorin-Nogueira , Idelmo Rangel Garcia-Júnior , Roberta Okamoto , The Journal of oral implantology. Volume: 40 Spec No, Issue: , 2014
Piezosurgery is a new and modern technique of bone surgery in implantology. Selective cutting is possible for different ultrasonic frequencies acting only in hard tissues (mineralized), saving vital anatomical structures. With the piezoelectric osteotomy technique, receptor site preparation for implants, autogenous bone graft acquistition (particles and blocks), osteotomy for alveolar bone crest expansion, maxillary sinus lifting, and dental implant removal can be performed accurately and safely, providing excellent clinical and biological results, especially for osteocyte viability. The aim of this review was, through literature review, to present clinical applications of piezosurgery in implant dentistry and outline their advantages and disadvantages over conventional surgical systems. Moreover, this study addressed the biological aspects related to piezosurgery that differentiate it from those of bone tissue approaches. Overall, piezosurgery enables critical operations in simple and fully executable procedures; and effectively, areas that are difficult to access have less risk of soft tissue and neurovascular tissue damage via piezosurgery. Read MorePiezoelectric bone surgery compared with conventional rotary instruments in oral surgery and implantology: Summary and consensus statements of the International Piezoelectric Surgery Academy Consensus Conference 2019., Francesco Bassi , Marco Cicciù , Roberto Di Lenarda , Pablo Galindo Moreno , Fabio Galli , Alan Scott Herford , Asbjørn Jokstad , Teresa Lombardi , Myron Nevins , Lars Sennerby , Gianmario Schierano , Tiziano Testori , Giuseppe Troiano , Tomaso Vercellotti , Claudio Stacchi , International journal of oral implantology (Berlin, Germany). Volume: 13, Issue: 3, 2020
PURPOSE
Piezoelectric bone surgery was introduced into clinical practice almost 20 years ago as an alternative method for cutting bone in dental surgical procedures, in an attempt to reduce the disadvantages of using conventional rotary instruments. The aim of this Consensus Conference was to evaluate the current evidence concerning the use of piezoelectric surgery in oral surgery and implantology.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Three working groups conducted three meta-analyses with trial sequential analysis, focusing on the use of piezoelectric surgery in impacted mandibular third molar extraction, lateral sinus floor elevation and implant site preparation. The method of preparation of the systematic reviews, based on comprehensive search strategies and following preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, was discussed and standardised.
RESULTS
Moderate/low evidence suggests that piezoelectric surgery is significantly associated with a more favourable postoperative course (less pain, less trismus) after impacted mandibular third molar extraction than conventional rotary instruments. Moderate evidence suggests that implants inserted with piezoelectric surgery showed improved secondary stability during the early phases of healing compared with those inserted using a drilling technique. Strong/moderate evidence suggests that piezoelectric surgery prolongs the duration of surgery in impacted mandibular third molar extraction, sinus floor elevation and implant site preparation, but it is unclear whether the slight differences in duration of surgery, even if statistically significant, represent a real clinical advantage for either operator or patient. Weak evidence or insufficient data are present to draw definitive conclusions on the other investigated outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Further well-designed trials are needed to fully evaluate the effects of piezoelectric surgery, especially in implant site preparation and sinus floor elevation. Read More